https://ultimate-energizer-guide.blogspot.com/2024/08/free-energy-power-from-pendulum.html
Veljko Milkovic’s Pendulum/Lever System
The general idea that it is not possible to have excess power from a purely mechanical device is clearly wrong as has recently been shown by Veljko Milkovic here where his two-stage pendulum/lever system shows a COP = 12 output of excess energy. COP stands for “Coefficient Of Performance” which is a quantity calculated by diving the output power by the input power which the operator has to provide to make the system work. This purely mechanical system has output power twelve times greater than the power needed to swing the pendulum. Please note that we are talking about power levels and not efficiency. It is not possible to have a system efficiency greater than 100% and it is almost impossible to achieve that 100% level.
Here is Veljko’s diagram of his very successful lever / pendulum system:
Here, the beam 2 is very much heavier than the pendulum weight 4. But, when the pendulum is set swinging by a slight push, the beam 2 pounds down on anvil 1 with considerable force, certainly much greater force than was needed to make the pendulum swing.
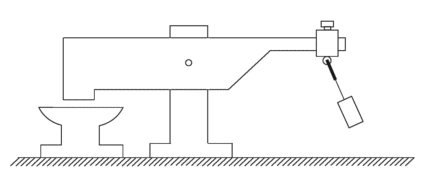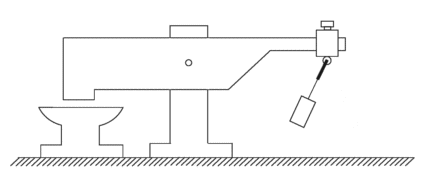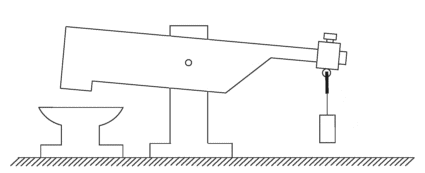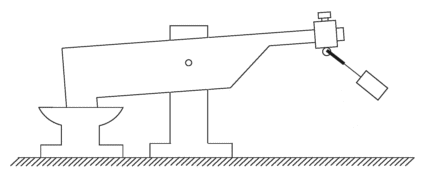
As there is excess energy, there appears to be no reason why it should not be made self-sustaining by feeding back some of the excess energy to maintain the movement. A very simple modification to do this could be:

Here, the main beam A, is exactly balanced when weight B is hanging motionless in it’s “at-rest” position. When weight B is set swinging, it causes beam A to oscillate, providing much greater power at point C due to the much greater mass of beam A. If an additional, lightweight beam D is provided and counterbalanced by weight E, so that it has a very light upward pressure on its movement stop F, then the operation should be self-sustaining.
For this, the positions are adjusted so that when point C moves to its lowest point, it just nudges beam D slightly downwards. At this moment in time, weight B is at its closest to point C and about to start swinging away to the left again. Beam D being nudged downwards causes its tip to push weight B just enough to maintain its swinging. If weight B has a mass of “W” then point C of beam A has a downward thrust of 12W on Veljko’s working model. As the energy required to move beam D slightly is quite small, the majority of the 12W thrust remains for doing additional useful work such as operating a pump.
🔺 A detailed step-by-step blueprint for creating a free energy generator:
It's Even More Practical Than It Seemed 70 Years Ago…
🔻 And for the first time in human history, ordinary folks can finally power up anything they need with renewable electricity...while investing a fraction of what the inventor ever thought was possible.
💠 Revealed At Last:👉 Ancient Invention Generates Energy-On-Demand