Inverter diagram Op-Amps Circuits Simple
An inverter is a device that converts DC power (battery) into AC power (usually sine or square waveform, 220V | 50HZ). Our conventional emergency power supplies typically convert battery DC to 220V AC. Simply put, an inverter is a device that converts direct current into alternating current. Whether you are in a remote village, need it in the wilderness, or have an emergency power outage, an inverter is a very good choice. More commonly, UPS power supplies are used in computer rooms. In the event of a sudden power outage, the UPS reverses the DC power in the battery to AC for use by the computer, thus preventing data loss due to a sudden power-off. This article will introduce two relatively simple inverter circuit diagrams. A simple inverter circuit diagram is attached. For those of you who are interested, being able to research and make your own inverter is truly a very satisfying thing. The following is a common inverter circuit diagram.
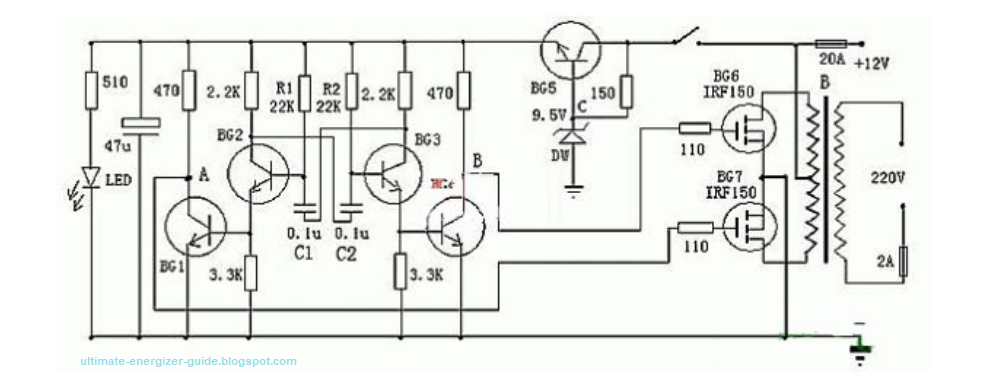
Above is an inverter circuit diagram that is relatively easy to make. It can invert 12V DC power voltage to 220V power voltage. The circuit is controlled by the harmonizer consisting of BG2 and BG3, and controlled by BG1 and BG4. BG6 controller works with BG7. The oscillator circuit is powered by the adjustable power supply of BG5 and DW groups, which can make the output frequency more stable. During production, the transformer can be selected from a conventional power transformer with dual 12V output. You can choose the appropriate 12V battery capacity according to your needs.
The following is the electrical diagram of a high-efficiency sine wave inverter.
The circuit is powered by a 12V battery. First, use a voltage doubler module to double the voltage to power the op-amp. You can choose ICL7660 or MAX1044. Op-amp 1 generates a 50Hz sine wave as a reference signal. Op-amp 2 acts as an inverter. Op-amp 3 and op-amp 4 act as delay comparators. Actually, op-amp 3 and switching tube 1 form a proportional switching power supply. The same thing happens with op-amp 4 and switch tube 2. Its switching frequency is unstable. When the output signal of op-amp 1 is positive phase, op-amp 3 and the switching tube are active. At this time, the output of op-amp 2 is negative phase. At this time, the input anode potential of op-amp 4 (constant) is always higher than the input cathode potential, so the output of op-amp 4 is always equal to 1 and the switch tube is turned off. When the output of op-amp 1 is negative phase, the opposite is true. This allows the two switching tubes to operate alternately.
Explanation of operating principle:
There are currently two types of inverters:
🔹 Version from Nikola Tesla's "Magnifying Transmitter"
🔹 The "tension" for "electricity fractionation" to occur is the Earth's Potential Potential. To be precise, it is the tension of the Ether, and the electricity is the dynamic polarization of the Ether.
🔹 During "Electricity segment", the magnetic field collapses several times in short periods of time. That leads the voltage V = Φ/t to reach infinity (V → ∞) when t → 0
- V - The electromotive force which results from the production or consumption of the total magnetic induction Φ (Phi). The unit is the “Volt”. Where t is the time of magnetic field collapse from maximum to complete collapse.
- Research scholars also call it Tesla's technology called Radiant Energy from Electronic Circuits, Impulse Technology.